Introduction
how many miles is the moon from earth Since the beginning of human history, people have looked up at the night sky and wondered about the Moon. It has inspired myths, guided travelers, shaped calendars, and played a key role in scientific discovery. Among the many questions asked about our closest celestial neighbor, one of the most common is simple yet fascinating: how many miles is the Moon from Earth?
The answer may seem straightforward at first, but the reality is more complex than a single number. The distance between Earth and the Moon changes constantly due to orbital mechanics, gravitational forces, and astronomical cycles. Understanding this distance opens the door to broader insights about space, motion, and the unique relationship between our planet and its natural satellite.
This article explores the exact distance in miles, why it changes, how scientists measure it, how long it takes to travel there, and why this distance is so important for life on Earth.
The Average Distance Between the Moon and Earth
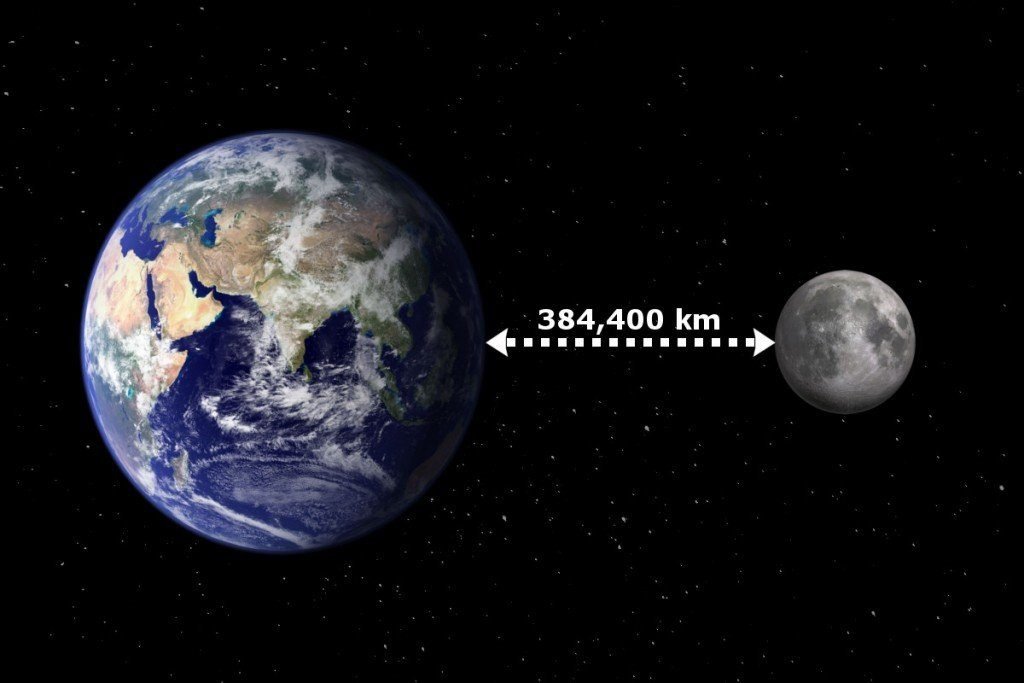
The average distance from Earth to the Moon is about 238,855 miles (384,400 kilometers). This number is widely accepted by astronomers and space agencies worldwide.
However, this figure represents an average because the Moon does not travel in a perfect circular orbit. Instead, it follows an elliptical path around Earth. This means the distance between the two bodies varies throughout the month.
When people ask how many miles is the Moon from Earth, they are usually referring to this average distance.
Why the Distance Changes Constantly
The Moon’s orbit is shaped like an oval rather than a circle. Because of this, there are two key points in its orbit that determine how far it is from Earth.
Perigee – The Closest Point
At its closest point, known as perigee, the Moon is approximately 225,623 miles from Earth. During this time, the Moon appears slightly larger and brighter in the night sky. This is often called a “supermoon.”
Apogee – The Farthest Point
At its farthest point, known as apogee, the Moon can be about 252,088 miles away. During this phase, it looks slightly smaller and dimmer.
Because of these variations, the exact answer to how many miles is the Moon from Earth depends on when the measurement is taken.
How Scientists Measure the Distance
Measuring the distance between Earth and the Moon has evolved dramatically over time.
Ancient Methods
Early astronomers estimated the distance using geometry, shadows, and observations of lunar eclipses. Greek astronomers were among the first to calculate a rough estimate, which was surprisingly close to modern measurements.
Modern Laser Technology
Today, scientists use highly accurate laser ranging techniques. During past lunar missions, astronauts placed reflective mirrors on the Moon’s surface. Scientists on Earth fire laser beams toward these reflectors and measure how long the light takes to return.
Since light travels at a known speed, this allows extremely precise calculations—accurate to within a few centimeters.
How Long Does It Take to Travel to the Moon?
Another common curiosity linked to how many miles is the Moon from Earth is travel time.
Spacecraft Travel Time
Most spacecraft take about 3 days to reach the Moon.
Apollo Missions
The historic Apollo missions followed a similar timeline. Astronauts typically reached lunar orbit within around 72 hours after launch.
Hypothetical Travel Speeds
If you could travel by car at highway speeds (around 60 mph), it would take more than six months of nonstop driving to reach the Moon.
If a commercial airplane attempted the journey, it would take nearly three weeks of continuous flight.
The Moon Is Slowly Moving Away
An interesting scientific fact is that the Moon is gradually drifting farther from Earth.
Due to tidal interactions between the two bodies, the Moon moves away at a rate of about 1.5 inches per year.
Although this seems tiny, over millions of years it significantly changes the distance. Billions of years ago, the Moon was much closer and appeared far larger in the sky.
Why the Distance Matters for Life on Earth
The Moon’s distance plays a crucial role in maintaining balance on our planet.
Tides
The gravitational pull of the Moon creates ocean tides. how many miles is the moon from earth If the Moon were much closer, tides would be dramatically stronger and could cause extreme coastal flooding.
If it were farther away, tides would be weaker, affecting marine ecosystems.
Earth’s Rotation Stability
The Moon stabilizes Earth’s tilt, which helps regulate climate patterns. Without this stabilizing effect, Earth’s seasons could fluctuate dramatically over time.
How the Moon Formed
Understanding how many miles is the Moon from Earth also connects to its origin.
The most widely accepted theory is the giant impact hypothesis. According to this idea, a Mars-sized object collided with early Earth billions of years ago. Debris from the collision eventually formed the Moon.
This explains why the Moon’s composition is similar to Earth’s outer layers.
How the Moon Appears from Earth
Despite being nearly a quarter million miles away, the Moon appears large in our sky.
This is because:
- It is relatively close compared to other celestial objects
- Its surface reflects sunlight efficiently
- Its size is large compared to Earth
This combination makes the Moon one of the most visually striking objects visible from Earth.
Comparing the Distance to Everyday Scales
To better understand how many miles is the Moon from Earth, it helps to visualize the distance.
- You could fit about 30 Earth-sized planets in a straight line between Earth and the Moon.
- The distance is roughly equivalent to circling Earth nearly 10 times.
- Light from the Moon takes about 1.3 seconds to reach Earth.
These comparisons help illustrate just how vast this distance truly is.
The Moon’s Role in Space Exploration
The relatively short distance between Earth and the how many miles is the moon from earth Moon makes it an ideal target for space exploration.
Because it is so close compared to other planets, it serves as a testing ground for technology, scientific experiments, and future missions deeper into space.
Scientists believe future lunar missions could lead to permanent research bases.
Cultural and Historical Importance
Beyond science, the Moon’s distance has fascinated how many miles is the moon from earth cultures worldwide.
Ancient civilizations tracked its motion to create calendars and guide agriculture. Its predictable orbit allowed early societies to measure time accurately.
Even today, the Moon continues to influence art, literature, and human imagination.
Future Changes in Distance
Although the Moon is slowly moving away, this process occurs over millions of years.
In the far future, Earth’s days will become longer how many miles is the moon from earth because tidal forces will slow the planet’s rotation. Eventually, the Moon will appear smaller in the sky.
However, this will take billions of years, far beyond human timescales.
Common Misconceptions About the Distance
There are several misunderstandings surrounding how many miles is the Moon from Earth.
It’s Not a Fixed Number
Many people assume the distance is constant, but it changes daily due to the Moon’s orbit.
It’s Not the Closest Object in Space
While it is Earth’s closest natural satellite, some human-made spacecraft have traveled farther in a short time.
The Moon Doesn’t Orbit Perfectly
Its path is influenced by gravitational interactions with Earth and the Sun.
Why People Are Still Curious Today
Even in the modern age, curiosity about the Moon remains strong.
People ask how many miles is the Moon from Earth because it connects science with everyday wonder. It reminds us how small we are compared to the universe, while also highlighting humanity’s ability to explore beyond our planet.
Conclusion
how many miles is the moon from earth The most accurate answer is that the average distance is about 238,855 miles, though it varies due to the Moon’s elliptical orbit.
This distance is more than just a number. It represents a delicate cosmic relationship that influences tides, stabilizes Earth’s climate, and enables space exploration. It has shaped human history, inspired scientific breakthroughs, and continues to fuel curiosity about the universe.
As we continue exploring space and planning future missions, the Moon will remain our closest gateway to the stars—forever reminding us of both our limits and our potential.

